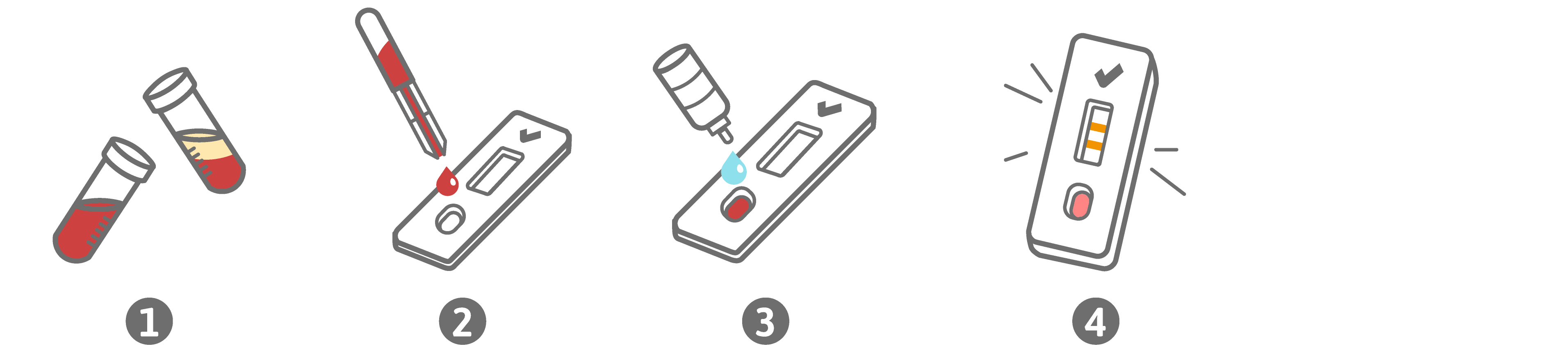
Only for sale to professional users such as doctors, pharmacists, alternative practitioners and other medically trained personnel.
Thrombosis and pulmonary embolism – a race against time!
Thrombosis is the formation of a blood clot (blood clot) in a blood vessel. A clinical distinction is made between arterial thromboses (infarcts) and venous thromboses (leg vein thrombosis, pulmonary embolism). Superficial venous thromboses can occur, for example, in the case of varicose vein disease, as well as in the case of lack of exercise or fluid, and can result in complications such as deep vein thrombosis or pulmonary embolism. In such cases, rapid diagnosis and therapeutic intervention are important and often even vital. Blood clots are formed by the build-up of a fibrin network. When this clot is broken down, fibrin degradation products are formed, the so-called D-dimers. These are considered indirect, early markers of clotting activity in thromboembolic diseases.