According to the WHO, colorectal cancer is the third most common cancer worldwide, with approximately 1.9 million new cases in 2020. In Germany alone, about 61.000 people are diagnosed with colorectal cancer every year, of which almost 25.000 die each year. The majority of these deaths could be prevented with appropriate screening, because colorectal cancer detected at an early stage is almost always curable!
PreventID® CC (Home)
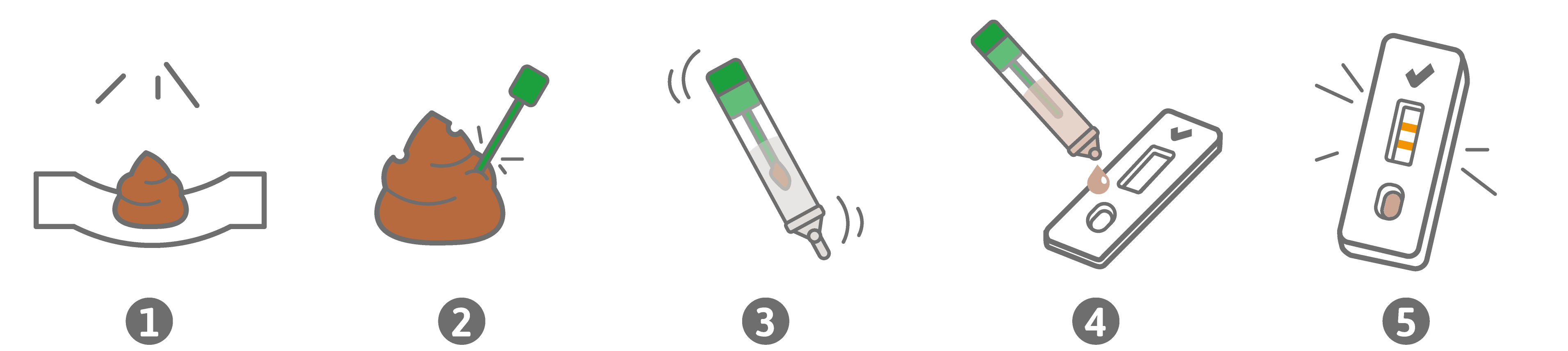
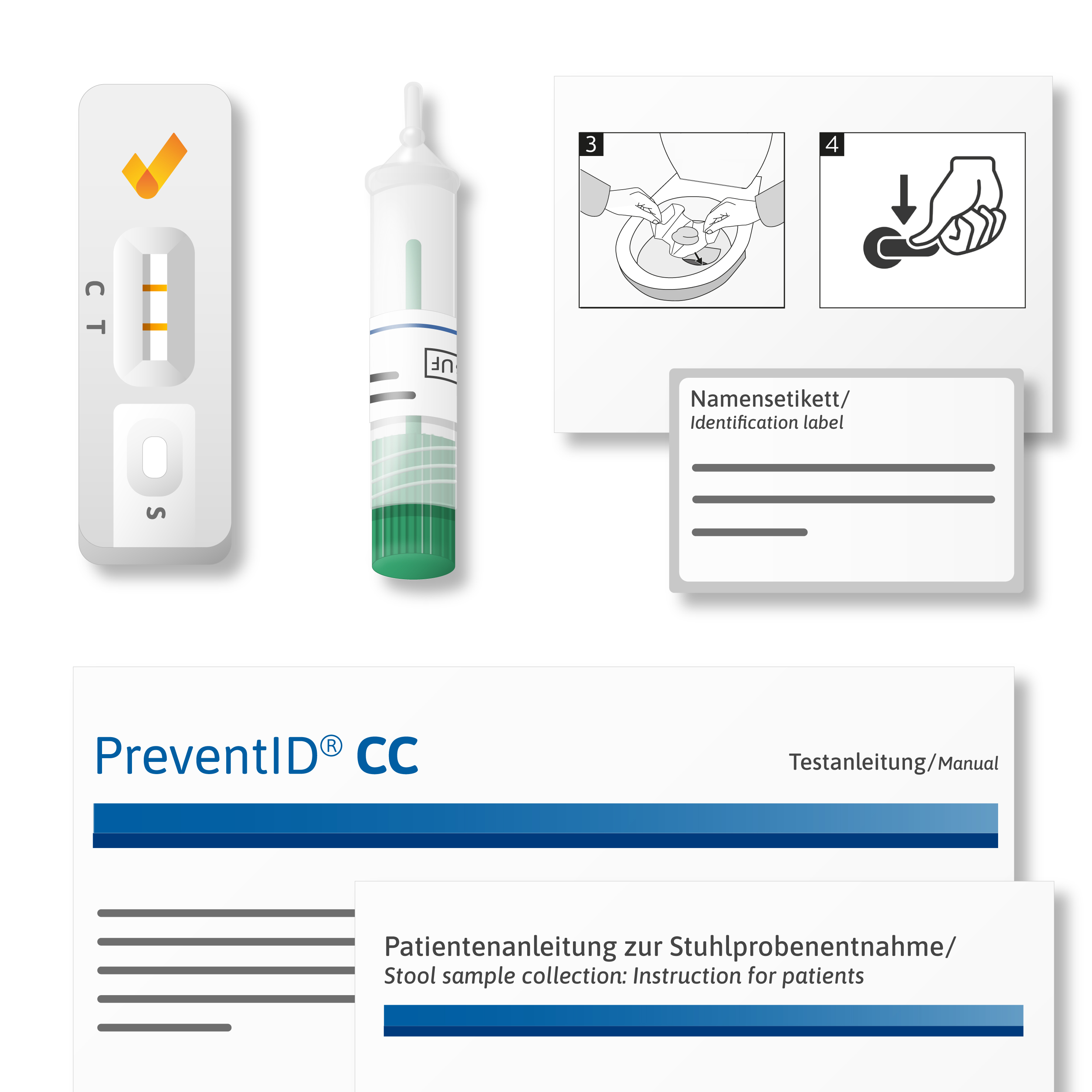
The immunological occult blood test PreventID® CC is a rapid test for self-testing for the qualitative detection of the valuable red blood pigment hemoglobin in stool as a marker for intestinal bleeding. The result can be read after 10 minutes.
For rapid and safe colorectal cancer screening in the practice or at home
Your benefits
- High reliability due to highest specificity
- Your patients do not need to follow a diet before use
- Patients can continue to take their usual medication
- Test results are available after a few minutes

Compared to colonoscopy
Relative sensitivity
75 %
Relative specificity
99 %
Detection limit
50 ng/ml
Downloads
Quellen:
- Bischoff-Ferrari HA. Optimal serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels for multiple health outcomes. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2008;624:55-71. doi:10.1007/978-0-387-77574-6_5;
- Panagiotou G, Tee SA, Ihsan Y, et al. Low serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25[OH]D) levels in patients hospitalised with COVID-19 are associated with greater disease severity. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2020:10.1111/cen.14276. doi:10.1111/cen.14276;
- Kimball SM, Mirhosseini N, Holick MF. Evaluation of vitamin D3 intakes up to 15,000 international units/day and serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentrations up to 300 nmol/L on calcium metabolism in a community setting. Dermatoendocrinol. 2017;9(1):e1300213. doi:10.1080/19381980.2017.1300213;
- Castillo ME, Costa LME, Barrios JMV, et al. Effect of calcifediol treatment and best available therapy versus best available therapy on intensive care unit admission and mortality among patients hospitalized for COVID-19: A pilot randomized clinical study. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2020;203:105751. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2020.105751.
