Colon Cancer – still a taboo topic:¹ ²
What is bowel cancer and how does the disease develop?² ³ ⁴ ⁵
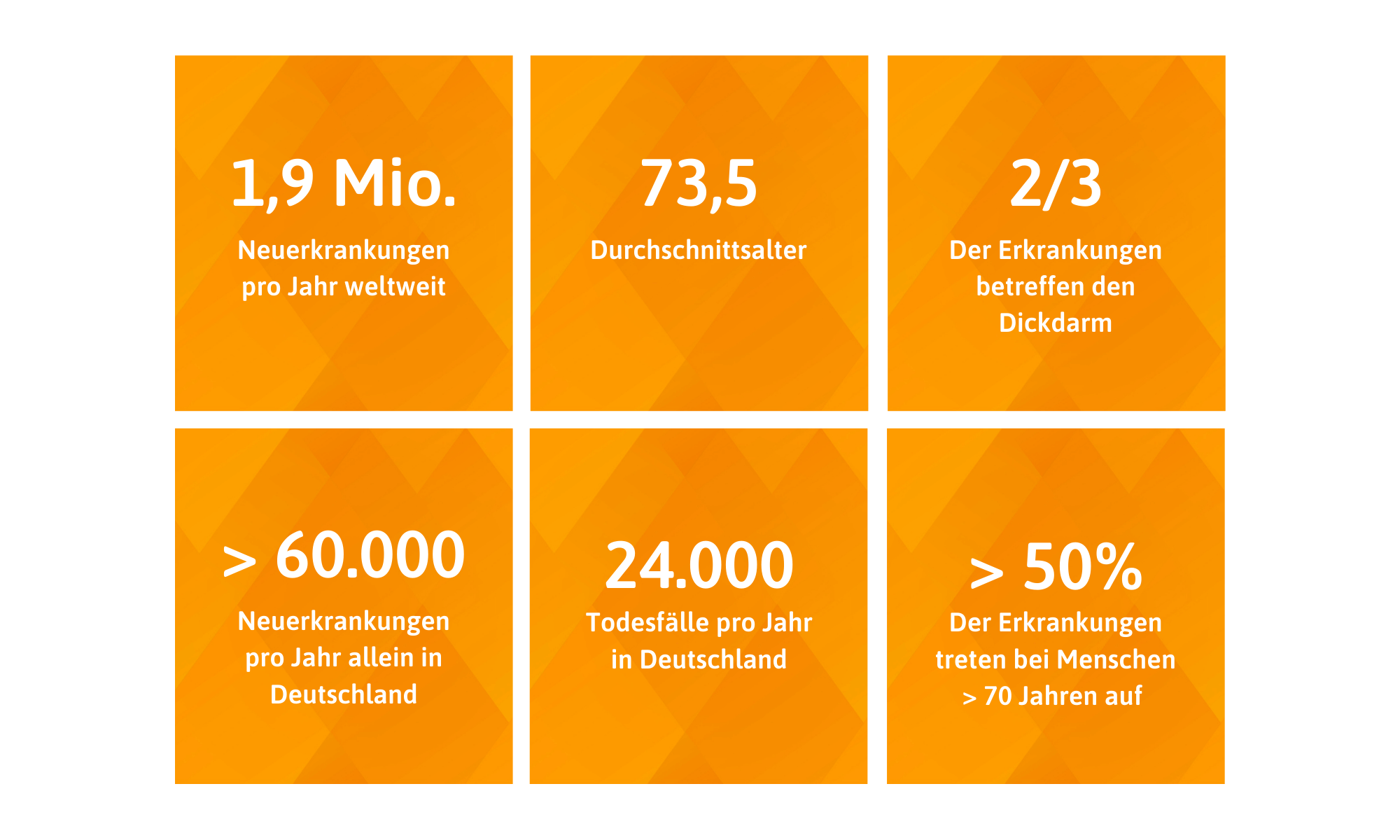
When we talk about bowel cancer, we usually mean tumours in the large intestine (colon) or in the rectum. Medically, these diseases are referred to as colorectal carcinomas. About one in eight cancers in Germany affect these parts of the intestine. Cancers in the small intestine, which is known to be directly connected to the stomach, are rather rare.
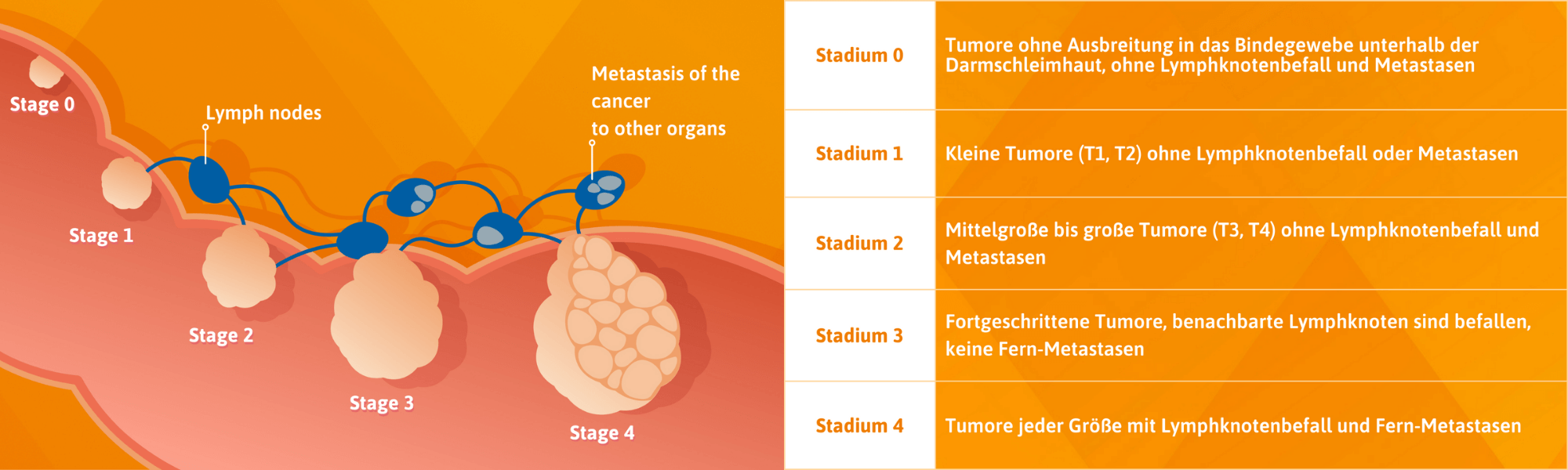
The exact causes for the development of bowel cancer have not yet been clarified in detail. What is known, however, is that a combination of different factors leads to excessive, uncontrolled cell growth in the intestinal mucosa, which in some cases leads to cancer. In most cases, colon cancer develops from growths in the intestinal mucosa, which are called polyps. These initially benign growths often go undetected for years because they rarely cause symptoms. Over time, these very small growths can grow and change or degenerate. However, not all polyps (adenomas) develop into malignant tumours (carcinomas). The severity of the disease is indicated by the Union Internationale Contre le cancer (UICC) by defining different stages of development:
What are the symptoms and signs?⁶
Bowel cancer is often only detected at a very late stage. But what is the reason for this? The main reason is that in the first years of the disease there are often no symptoms at all. The first signs of bowel cancer, if present, are usually rather unspecific and are accompanied by ambiguous symptoms such as fatigue and unexplained weight loss. In the course of the disease, a wide variety of symptoms then appear:
- Altered bowel movements (constipation, diarrhea, pain during bowel movements)
- Frequent urge to have a bowel movement
- Change in the appearance of the stool, reddish or dark discoloration, blood in the stool
- Digestive problems
- Abdominal pain
- Foul-smelling stools
- Feeling that the bowel is not emptying completely
- Flatulence
If the tumor is already more advanced, the symptoms change, and other signs of illness may occur:
- Tiredness, fatigue, reduced physical performance
- Paleness due to anaemia
- Nausea, vomiting
- Mild fever
- Cramps
- Radiating pain in the pelvis or lumbar spine, often perceived as back pain
- Intestinal obstruction
If the tumor is already more advanced, the symptoms change, and other signs of illness may occur:
Iedereen kan de diagnose darmkanker krijgen. Toch zijn er bepaalde factoren die het risico op het ontwikkelen van darmkanker verhogen. De belangrijkste risico's zijn bijvoorbeeld tabaks- en alcoholgebruik, zwaarlijvigheid, gebrek aan lichaamsbeweging en een slecht dieet (weinig vezels, veel rood vlees). Familiale factoren spelen ook een rol - mensen met getroffen familieleden hebben een dubbel tot driedubbel risico om ook de ziekte te krijgen. Chronische inflammatoire darmziekten, zoals de ziekte van Crohn of colitis ulcerosa, bevorderen ook de ontwikkeling van darmtumoren. Tenslotte spelen ook leeftijd en geslacht een grote rol bij het onderwerp darmkanker. Mannen worden iets vaker getroffen dan vrouwen - het levenslange risico om darmkanker te krijgen is 5,3% voor vrouwen en 6,5% voor mannen. Dit betekent dat één op de 15 mannen en één op de 19 vrouwen tijdens hun leven de diagnose darmkanker zal krijgen. Het risico om de ziekte te krijgen blijft stijgen tot op hoge leeftijd. Meer dan de helft van de patiënten ontwikkelt de ziekte na de leeftijd van 70 jaar, en de gemiddelde leeftijd waarop de ziekte begint is 75 (vrouwen) of 72 (mannen). Slechts één op de tien gevallen doet zich voor vóór de leeftijd van 55 jaar.
Life expectancy/curability/prevention:¹ ² ⁸
By 2020, it is estimated that almost 1 million people worldwide will have died of colorectal cancer. The relative 5-year survival rate for colorectal cancer patients in Germany is 65% (women) and 63% (men). If the cancer is diagnosed at an early stage, i.e. at best before symptoms appear, the chances of cure and thus life expectancy increase significantly. If the disease is diagnosed at stage I, about 92-95% of those affected survive the first 5 years after diagnosis. Efficient prevention through early detection measures can prevent 40-60% of cancer cases and deaths.
How can I prevent it?⁷
Even if we cannot influence certain factors, such as a genetic predisposition or chronic diseases of the intestinal tract, a healthy lifestyle still contributes significantly to the prevention of bowel cancer. In addition to a healthy diet and plenty of exercises, experts recommend avoiding alcohol and tobacco. Last but not least, prevention through early detection measures such as colonoscopy or tests for occult (hidden) blood in the stool is important for early diagnosis and thus efficient treatment. Regular colorectal cancer screening is also recommended for people under 50 years of age, especially if they have a family history of the disease.